Beyond Algorithms: Championing Unbiased Digital Realms
Using GPT-4 for Content Moderation: A Deep Dive
OpenAI has recently unveiled a novel approach to content moderation by leveraging the capabilities of GPT-4. This article delves into the intricacies of this approach and its implications for the digital world.
The Need for Content Moderation
Content moderation is paramount for maintaining the integrity and health of digital platforms. Traditional methods rely heavily on human moderators who painstakingly sift through vast amounts of content to filter out harmful or toxic material. This process is not only time-consuming but also mentally taxing for the moderators. With the advent of GPT-4, OpenAI aims to revolutionize this space.
GPT-4: The Game Changer
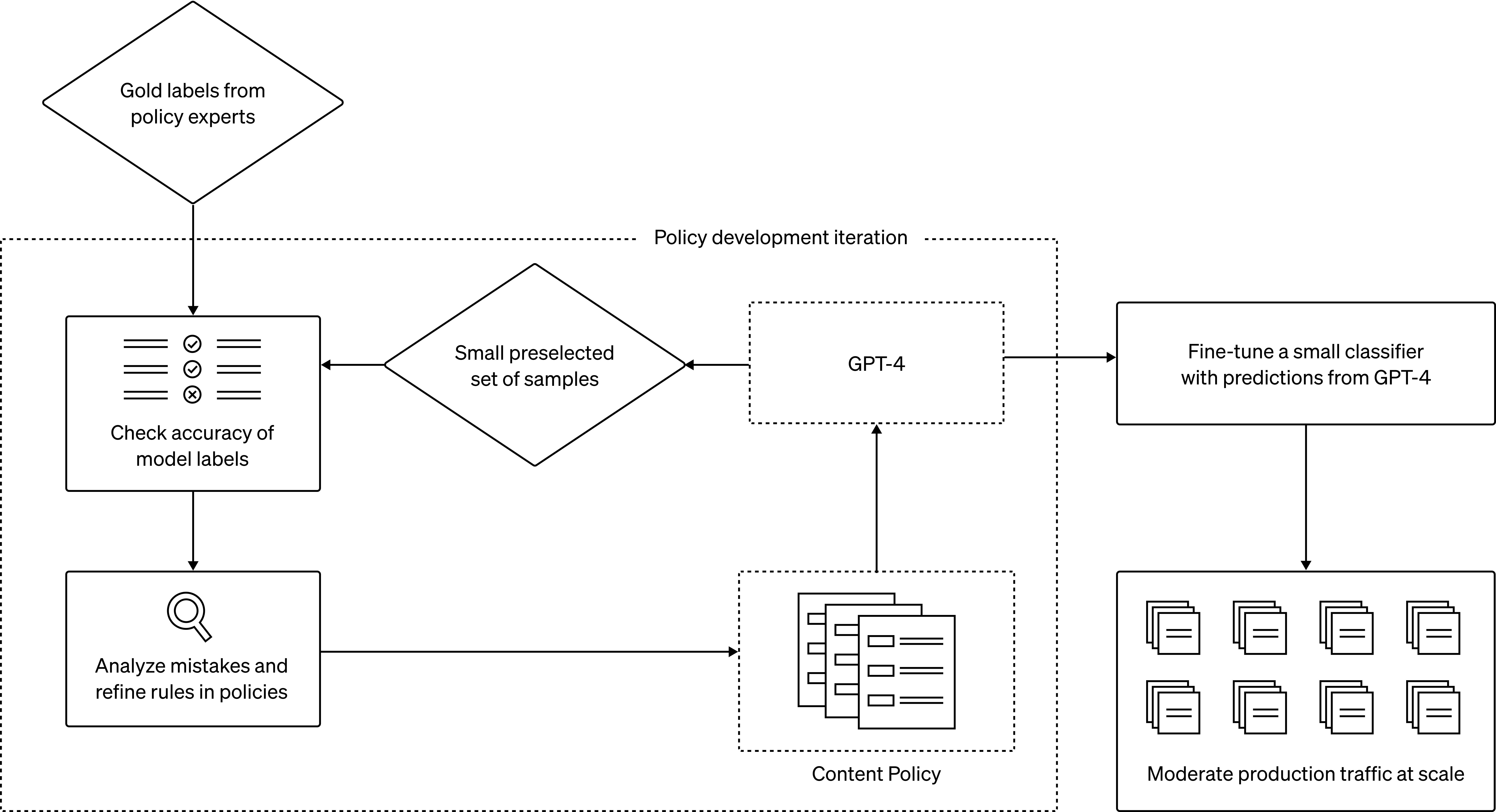
GPT-4, a large language model, can understand and generate natural language, making it apt for content moderation tasks. The model can:
- Interpret and adapt to long content policy documentation instantly.
- Reduce the policy change iteration cycle from months to mere hours.
- Provide consistent labeling by understanding the nuances in policy documentation.
The process begins with policy experts creating a “golden set” of data by labeling a few examples according to the policy. GPT-4 then reads the policy and assigns labels to the same dataset without prior knowledge of the answers. Discrepancies between human and GPT-4 judgments are analyzed, leading to policy refinements. This iterative process eventually results in refined content policies that can be deployed at scale.
Advantages Over Traditional Methods
- Consistency: Human interpretation of policies can vary, leading to inconsistent labeling. GPT-4, sensitive to granular differences in wording, can adapt instantly to policy changes, ensuring a consistent user experience.
- Speed: The traditional cycle of policy updates can be lengthy. GPT-4 can condense this process to a few hours, allowing for rapid responses to emerging threats.
- Wellbeing: Continuous exposure to harmful content can be detrimental to human moderators. Automating this task alleviates the mental burden.
Challenges and Limitations
While GPT-4 offers a promising solution, it’s not without challenges. Language models can sometimes exhibit biases introduced during training. It’s crucial to monitor and validate their outputs, keeping humans in the loop, especially for complex edge cases. OpenAI remains committed to transparency and will continue to share its progress with the community.
In Conclusion
OpenAI’s approach to content moderation using GPT-4 offers a glimpse into the future of digital platforms. By reducing the reliance on human moderators and speeding up the policy iteration process, GPT-4 promises a safer and more consistent online experience.
Thought-Provoking Questions:
- The Human-AI Collaboration: How will the collaboration between human moderators and AI models like GPT-4 shape the future of content moderation?
- Bias in AI: How can we ensure that AI models like GPT-4 remain unbiased and make fair judgments?
- The Future of Digital Platforms: With AI taking a front seat in content moderation, how will digital platforms evolve to ensure safety and consistency?
For those interested in further details, the original article can be found on OpenAI’s blog.
The collaboration between human moderators and AI models like GPT-4 is poised to redefine the landscape of content moderation in several significant ways:
-
Efficiency and Scale: AI models can process vast amounts of data at a speed that’s impossible for humans. By handling the bulk of content moderation tasks, AI can free up human moderators to focus on more nuanced or complex cases. This means platforms can moderate content more quickly and at a larger scale.
-
Consistency: One of the challenges with human moderators is ensuring consistent decisions across the board, especially when policies are open to interpretation. AI models, once trained, can provide consistent judgments based on the guidelines they’ve been given, reducing variability in content moderation decisions.
-
Rapid Adaptation: As online content and user behaviors evolve, content moderation policies need to be updated. AI models like GPT-4 can adapt to new guidelines almost instantly, ensuring that content moderation remains up-to-date with the latest policies.
-
Reduced Mental Burden: Content moderation can be mentally taxing, especially when moderators are exposed to harmful or offensive content. By automating a significant portion of this work, the emotional and psychological stress on human moderators can be reduced.
-
Feedback Loops: The collaboration can create a feedback loop where human moderators provide feedback on AI decisions, which in turn helps refine and train the AI model further. This continuous learning process can lead to progressively better content moderation over time.
-
Handling Edge Cases: While AI can handle the majority of content, there will always be edge cases or nuanced situations that require human judgment. Human moderators will play a crucial role in these scenarios, ensuring that the final decision aligns with the platform’s values and policies.
-
Transparency and Trust: As AI models play a more significant role in content moderation, platforms will need to ensure transparency in how these models operate. Collaborating with human moderators can provide a layer of oversight and accountability, building trust with the user base.
-
Training and Refinement: Human moderators can play a pivotal role in training AI models. By providing labeled data, feedback, and insights, they can help refine the AI’s understanding and improve its accuracy over time.
In conclusion, the collaboration between human moderators and AI models like GPT-4 will lead to a more efficient, consistent, and adaptive content moderation system. While AI will handle the bulk of the tasks, humans will remain integral, providing oversight, handling complex cases, and ensuring that the system aligns with the platform’s values and goals.
Ensuring that AI models like GPT-4 remain unbiased and make fair judgments is a multifaceted challenge. Here are several strategies and best practices to address this:
-
Diverse Training Data: The biases in AI models often stem from the data they are trained on. By ensuring that the training data is diverse and representative of various perspectives, cultures, and backgrounds, we can reduce the chances of the model inheriting biases.
-
Regular Audits: Periodically auditing the AI’s decisions against a set of predefined fairness metrics can help identify and rectify biases. These audits should be conducted by diverse teams to ensure multiple perspectives are considered.
-
Feedback Loops: Implementing feedback mechanisms where users and human moderators can flag biased or unfair judgments by the AI can be invaluable. This feedback can be used to continuously refine and retrain the model.
-
Transparency: Making the workings of the AI model transparent, to the extent possible, can allow external experts and the community to scrutinize and identify potential biases. Open-sourcing certain aspects or providing detailed documentation can aid in this.
-
Ethical Guidelines: Establishing clear ethical guidelines for AI development and deployment can set the standard for fairness and unbiased behavior. These guidelines should be regularly updated to address emerging challenges.
-
Human Oversight: Even with advanced AI models, human oversight remains crucial. Humans can review and override AI decisions, especially in ambiguous or sensitive cases, ensuring that the final judgment aligns with fairness principles.
-
Bias Mitigation Techniques: There are various algorithmic techniques designed to reduce bias in AI models, such as re-weighting training examples or adjusting decision thresholds. These can be employed to make the model’s outputs more fair.
-
Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging with a diverse group of stakeholders, including marginalized communities, can provide insights into potential biases and ways to address them. This engagement can take the form of consultations, surveys, or partnerships.
-
Continuous Learning: The digital landscape and societal norms evolve over time. AI models should be designed to continuously learn and adapt to these changes, ensuring that their judgments remain fair and relevant.
-
Education and Training: Developers, data scientists, and other stakeholders involved in the AI development process should be educated about the potential biases and ethical considerations. This can foster a culture of responsibility and vigilance.
-
External Partnerships: Collaborating with external organizations, NGOs, or academic institutions can provide third-party perspectives and expertise in identifying and addressing biases.
In conclusion, ensuring fairness and reducing bias in AI models like GPT-4 requires a combination of technical, organizational, and societal measures. It’s an ongoing process that demands vigilance, transparency, and a commitment to ethical principles.
The integration of AI in content moderation is reshaping digital platforms. As AI takes a more prominent role, here’s how digital platforms might evolve to ensure safety and consistency:
-
Real-time Moderation: With AI’s ability to process vast amounts of data quickly, content can be moderated in real-time. This means harmful or inappropriate content can be flagged or removed almost instantly, ensuring a safer online environment.
-
Personalized User Experience: AI can tailor content moderation based on individual user preferences and behaviors, ensuring a more personalized and relevant user experience while maintaining platform safety standards.
-
Adaptive Policies: AI can help platforms adapt their content policies more rapidly in response to emerging trends, challenges, or threats. This adaptability ensures that platforms remain current and responsive to the ever-changing digital landscape.
-
User Feedback Integration: Platforms might develop mechanisms for users to provide feedback on AI moderation decisions. This feedback can be used to refine the AI’s algorithms, ensuring that the system aligns with user expectations and values.
-
Transparency Tools: To build trust, platforms may offer tools that explain AI moderation decisions to users. This transparency can demystify the AI’s workings and foster a sense of accountability.
-
Human-AI Collaboration: While AI will handle the bulk of moderation tasks, human moderators will still play a crucial role, especially for complex or sensitive cases. Platforms might develop systems where AI and humans work in tandem, combining the efficiency of AI with the nuance and judgment of humans.
-
Enhanced Reporting Mechanisms: AI can assist in developing more sophisticated reporting tools for users, allowing them to specify the nature of the issue in detail. This can lead to more accurate and timely responses to user concerns.
-
Proactive Harm Detection: Beyond just content moderation, AI can be trained to proactively detect and mitigate potential harms, such as cyberbullying, misinformation, or coordinated harmful campaigns.
-
Diverse Training and Audits: To ensure consistency and fairness, platforms might invest in training their AI models on diverse datasets and conducting regular audits to check for biases or inconsistencies.
-
Community Engagement: Platforms may engage more with their user communities, seeking input on moderation policies and AI behavior. This collaborative approach can ensure that the platform aligns with the broader community’s values and expectations.
-
Ethical Standards: As AI becomes more integral to content moderation, platforms might adopt clear ethical standards for AI deployment, ensuring that user rights, privacy, and safety are prioritized.
-
Continuous Learning and Updates: AI models will be designed to continuously learn from their interactions and feedback. Regular updates will ensure that the AI remains effective and relevant in its moderation tasks.
In conclusion, as AI becomes central to content moderation, digital platforms will likely become more adaptive, transparent, and user-centric. The challenge will be to strike the right balance between automation and human touch, ensuring safety and consistency while respecting user rights and freedoms.



Comments